Two options for waking up a thread: Directly granting the lock vs Re-fairly competing for the lock
Monitor - Hoare
- 1. T1 enters the monitor
- 2. T1 waits for resources (enters the wait queue)
- 3. T2 enters the monitor
- 4. T2 resources are available, notify T1 to resume execution,
and transfer yourself to the urgent waiting queue
- 5. T1 re-enters the monitor and executes
- 6. T1 leaves the monitor
- 7. T2 re-enters the monitor and executes
- 8. T2 leaves the monitor
- 9. Other threads in the entry queue pass the competition
Enter the monitor monitor
Monitor - Mesa
- 1. T1 enters the monitor
- 2. T1 waits for resources
(Enter the wait queue and release the monitor)
- 3. T2 enters the monitor
- 4. T2 resources are available, notify T1
(T1 is transferred to the entey queue and competes on an equal footing again)
- 5. T2 continues execution
- 6. T2 leaves the monitor
- 7. T1 obtains the execution opportunity from the entry queue
Dequeue, resume execution
- 8. T1 leaves the monitor
- 9. Other threads in the entry queue pass the competition
enter monitor
Monitor - Hansen
- 1. T1 enters the monitor
- 2. T1 waits for resource c
- 3. T2 enters the monitor
- 4. T2 leaves Monitor and waits for notification
The thread of resource c, the resource is available
- 5. T1 re-enters the monitor
- 6. T1 leaves the monitor
- 7. Other threads pass the competition from the entry queue
enter monitor
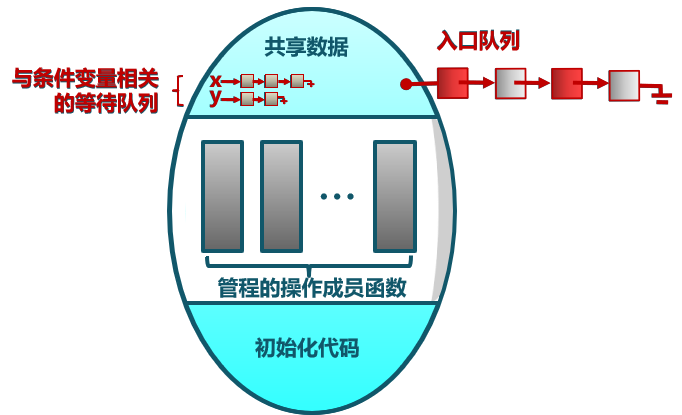
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Implementation of condition variables
Monitor -- Producer-consumer problem
Monitor -- Producer-consumer problem
Monitor -- Producer-consumer problem
Monitor -- Producer-consumer problem
Gregory Kesden, Monitors and Condition Variables https://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse120-a/applications/ln/lecture9.html
Mark Spruiell, The C++ Monitor Class. Apr. 2011 https://doc.zeroc.com/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=5048235
wikipedia, Monitor (synchronization) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monitor_(synchronization)
Mike Vine, Making a C++ class a Monitor (in the concurrent sense) https://stackoverflow.com/a/48408987
David Rodríguez - dribeas, How arrow-> operator overloading works internally in c++? https://stackoverflow.com/a/10678920
Fruit_初, Monitors, March, 2017. https://www.jianshu.com/p/8b3ed769bc9f
C++ Concurrency Pattern #6: Monitor - monitor http://dengzuoheng.github.io/cpp-concurency-pattern-6-monitor
https://blog.csdn.net/Carson_Chu/article/details/104223122 [Operating System] Synchronization Mutual Exclusion Mechanism (2): Monitor and Inter-Process Communication Mechanism (IPC)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/465751547 This article is enough for learning process mutual exclusion and process synchronization!
https://www.cnblogs.com/uestcliming666/p/13224545.html "Modern Operating System" - Chapter 6 Synchronization Mutual Exclusion Mechanism (2), Inter-process Communication Mechanism
https://yangzhaoyunfei.github.io/monitors/ Monitors
Release the power of the monitor, enter the conditional waiting queue of c; wake up the first thread in the emergency waiting queue // allocate some type of resource for the process entering the monitor, if this resource is available at this time, then the process Use, otherwise the process is blocked and enters the conditional waiting queue
Wake up the process that enters the conditional waiting queue due to waiting for this resource (c’s conditional waiting queue) The first thread enters the process of the monitor to release a certain resource. At this time, the process will wake up and enter the conditional waiting queue due to waiting for this resource Waiting for the first process in the queue
---
### monitor -- condition variable
- Synchronization: Condition Variables (Condition Variables) and related two operations: wait and signal, handle the waiting mechanism.
- Wait() operation
- Block yourself in the waiting queue
- Release the mutex access of the monitor
- Call in a process waiting outside the monitor
- Signal() operation
- Wake up a thread in the waiting queue
- Equivalent to a no-op if the wait queue is empty